Monero (XMR) is currently the largest anonymous cryptocurrency. Every now and then another anonymous coin like Verge enters the playing field, but Monero seems intangible and always working on its growth. It is a safe, untraceable and protected cryptocurrency. In this article you will find a detailed explanation about this popular cryptocurrency.
Read quickly
- What is Monero?
- How did Monero originate?
- The unique properties of Monero
- How does a Monero transaction work?
- About the coin XMR
- MoneroV fork
- How do I buy Monero (XMR)?
What is Monero (XMR)
Monero is a secure currency system that makes transactions untraceable. The cryptocurrency uses a special cryptography that assures the user that all his transactions are 100% untraceable and cannot be linked to his identity. You can therefore make completely anonymous transactions with Monero.
Due to the growing awareness that privacy is being compromised, Monero is very popular.
How did Monero originate?
The cryptocurrency Bytecoin was launched in mid-2012. This was the first currency CyptoNote implemented. CryptoNote is a protocol that many anonymous cryptocurrencies work with, because it provides more anonymity than, for example, Bitcoin.
People had a high hat on Bytecoin, but more and more suspicious things came to light, which reduced confidence in the currency. For this reason, it was decided to fork (fork) the Bytecoin blockchain and start its own coin and chain: Bitmonero. Eventually this name was changed to Monero, which means ‘coin’ in Esperanto.
Who founded this cryptocurrency?
The CryptoNote protocol on which Monero is based was launched by the man who goes through life under the pseudonym Nicolas van Saberhagen.
Monero was founded by a user on the Bitcointalk forum. His username on this platform is ‘Thankful_for_today’.
The top of Monero today consists of seven developers, five of whom wish to remain anonymous. David Latapie and Riccardo Spagni are the public face of the cryptocurrency and the other five are active on the internet under the names Smooth, Othe, NoodleDoodle, TacoTime and Elzh.
The project is open-source, so many other developers are still working on the anonymous cryptocurrency.
What makes Monero so special?
The CryptoNote protocol offers Monero four unique features:
1. The coin you own is really yours
You have complete control over your transactions. Your identity is private and no one in the world can find out what you do with your money.
2. It is replaceable
Substitutability means that a product can be interchanged with a product of the same type. To give an example:
If you borrow € 10 from your father and return it with another € 10 note, then that is not a problem. You can even give five €2 coins without hearing a word about it. But, if you borrow a bicycle from your father and return another bicycle the next day, you will still get a surprised reaction. The replaceability of a euro is therefore better than that of a bicycle.
Why is that fungibility important for a cryptocurrency?
When we look at Bitcoin, we see that it is a public blockchain. Everyone can view executed transactions and they will always be able to be found. It is therefore somewhat possible to track Bitcoins. You may now own Bitcoin that was once used for an illegal transaction. Suppose a major drug lord is arrested and it can be seen that one of his Bitcoins is now in your wallet, then you actually have an infected Bitcoin. Who would want to trade their own nice ‘clean’ Bitcoin for a dirty ‘contaminated’ Bitcoin? It can cause the infected Bitcoin to be seen as inferior to other Bitcoins. This affects the fungibility of this cryptocurrency. This is strange, because why should you pay for the illegal activities of that drug lord? Monero agrees and has succeeded in ensuring fungibility. The data and transactions of the coin are private and no one can see anything about it. The problem of infected coins is therefore not an issue.
3. Dynamic scalability
Monero miners, unlike Bitcoin, do not have a predetermined block size limit. Thanks to this dynamic scalability, the network cannot become overcrowded quickly, as was the case with Bitcoin (which could take hours to send a Bitcoin and also cost a lot of money). A danger of dynamic scalability is that miners allow the blocks to become very large (because this yields more for them), but to prevent this, the protocol works with a block reward penalty. This works as follows:
- The median is taken from the last 100 blocks and is called the M100.
- A new block of a certain size is mined, which is called the New Block Size (NBS).
- If the NBS is greater than the M100, the block reward is reduced depending on how far the NBS deviates from the M100. If the NBS is 10%, 50%, 80%, 100% greater than M100 then the reward will be reduced by 1%, 25%, 64%, 100% respectively. Miners will therefore not easily choose to make the block size larger than the M100.
4. Multiple keys
Monero does not only work with one private key and one public key, like most cryptocurrencies, but with a public and private view key and a public and private send key.
Public and private view key
The view key is mainly focused on the recipient of a transaction. The public view key is used to send money and the private view key is used to access these obtained coins.
Public and private spend key
The spend key is mainly aimed at the sender of a transaction. The public spend key ensures that the sender can participate in the ring transaction (more on this later) and also verifies the signature of the key image (more on this later). The private spend key helps create the key image making it possible to send transactions.
The Monero address
The Monero address consists of two parts. The public view key forms the first part of the address and the public spend key forms the second part. The address consists of 95 characters in total.
How does a Monero transaction work?
According to Monero, an electronic transaction must meet three requirements:
- It’s electronic
- It’s decentralized
- It is private/screened
Monero wants to operate by these criteria and strives to be completely private and opaque. The privacy of the sender is guaranteed by so-called Ring Signatures.
Cryptography #1: Ring Signatures
When you send someone a check, you must sign it with your signature. Anyone who views this check and recognizes your signature will know that you signed it. But, what if you pick five different people from the street and you merge everyone’s signatures and form a new signature in this way. No one will then be able to find out whether you were the one who signed this check. This is how a Ring Signature works. One question that immediately comes to mind is:
If it cannot be recognized, how can it prevent the same Monero coin from being spent twice?
Double spending
Miners have the role of preventing people from spending the same Monero coin twice, also known as double spending. Miners normally do this by blocking the transaction and using the sender’s public address so they know from which address money is being sent. At Monero this is not possible due to the Ring Signatures so they have found a new way.
Unique key image
Every transaction of the anonymous crypto coin comes with its own key image. This is unique for that one transaction and on the basis of this the miners can prevent the same Monero coin from being spent again. The following video clearly explains this concept:
Thus, the sender’s privacy is protected by Ring Transactions. How is the recipient’s protected?
Cryptography #2: Stealth Addresses
The recipient has two public keys, the public view key and the public spend key. To receive the transaction, the sender will use both of these public keys. A unique public key is generated from these two keys, which is only valid for that transaction. Another unique public key will be generated from these two for a subsequent transaction. The formula used for this is:
P = H(rA)G + B
|
The letters represent |
|
|
P |
public key |
|
r |
Random number chosen by the broadcaster |
|
a |
Public view key of the receiver |
|
G |
cryptographic constant |
|
B |
Recipient’s public spend key |
|
H () |
The Keccak hashing algorithm used by Monero |
Cryptography #3: Ring Confidential Transactions
We have seen how the privacy of the sender and the recipient is ensured. To make it completely watertight, it is wise to also leave the amount of coins that are transferred with a transaction unknown. They made this possible by implementing Ring Confidential Transaction. This protocol makes it possible to hide the number of Monero coins being sent. The following video explains how Monero’s transactions were in the early days and how the protocol has changed this:
An extra layer of protection
Monero is working on the ability to hide your internet behavior. As a result, not only the transactions, but also the actual use of Monero are hidden from the outside world. No one will know that you have ever looked at the platform.
They want to achieve this extra protection by integrating the implementation of I2P with Monero’s code. I2P, or Invisible Internet Project, is a decentralized and anonymous communication network that works on top of the normal internet, as a kind of extra layer. Everyone can browse anonymously, share files, chat, etc. Kovri is a C++ implementation of such an I2P network and Monero will use it.
In the Roadmap you can see that they are releasing an alpha release for this soon.
The Monero coin, XMR
Characteristics
|
Coin abbreviation |
XMR |
|
Number of coins in circulation |
15,779,080 |
|
Total number issued |
18,400,000 |
|
Coins are released by |
Mining (Proof-of-Work) |
Mining monero
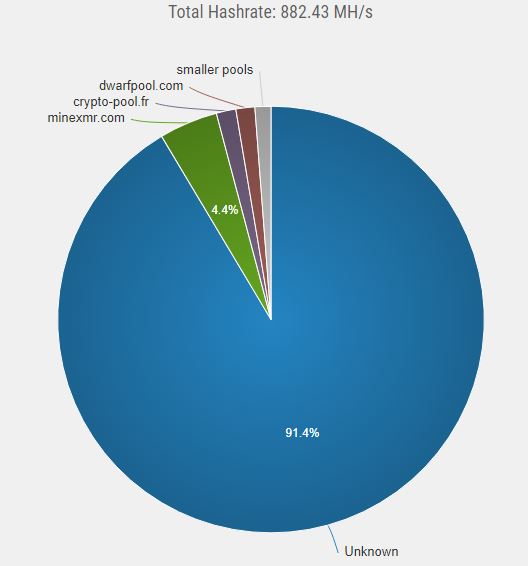
XMR mining is based on the CryptoNight Proof-of-Work algorithm, which comes from the CryptoNote protocol. The hashing algorithm is called CryptoNight. This algorithm is built to be ASIC resistant. With this they try to prevent mining pools from gaining power and the coins are not distributed fairly. On Monerohash you can find what the hashrate distribution is now. At the time of writing, we see that the vast majority of the hashrate is used by unknown users.
The last coin is expected to be mined on May 31, 2022. You can read here how to mine Monero yourself.
MoneroV fork
Monero is expected to undergo a hard fork on March 14, 2018. Anyone who owns the anonymous crypto coin during block height 1529810 will receive 1:10 MoneroV. So for every XMR you will be credited with 10 MoneroV. It may take a few days before you actually see them on the balance sheet.
When you have XMR on the exchange, it is unclear whether you will receive the MoneroV. This depends on the exchange. To make sure you benefit from the hard-fork, you can put the coins on the Monero wallet itself.
Curious what the new coin will bring us? Then you can read the MoneroV Roadmap here.
Would you like to buy Monero (XMR) so that you can benefit from the hard fork? Then follow the steps below:
How do I buy Monero?
Buying Monero on Binance is a piece of cake. With this explanation you will be the proud owner of XMR within a few steps.
- Sign up for free at Binance here
- Login to your account
Please note: keep your username and password safe! - Press Buy Crypto at the top left and choose Bank Deposit
- Fiat tab instead of Crypto and check that it ‘s on Euro
- Choose iDEAL if you want the money directly on your account and Bank Transfer (SEPA) if you also like it if it takes a few days before the money is on your account
- Wait until your euros have been deposited into the Binance account
- Click on Trading at the top and select Classic
- You are now on the trading section of Binance. Click on FIAT on the right and select EUR
- A number of coins can be traded on Binance for euros. But, most of them are traded against Bitcoin. Look up the trading pair BTC/EUR and buy Bitcoin with your euros.
- BTC tab and look up Monero using its ticker XMR
- BTC/XMR trading pair . By clicking on it, you can buy Monero
- Congratulations! You are in possession of your favorite cryptocurrency!
Sources: Blockgeeks, Wikipedia, Youtube, GetMonero

